
What is Vitamin D;
Vitamin D also known as calciferol is a fat-soluble vitamin found naturally in some foods, added to others and is available as a supplement. It is also a hormone that our body produces endogenously when our skin is exposed to UV rays from sunlight.
Vitamin D Properties
Bone Health
The presence of vitamin D is essential for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the intestine. The proper absorption of both minerals is vital for strong and healthy bones. No matter how much calcium we get from our diet, it will not be absorbed if we do not get enough vitamin D.
Anti-inflammatory Activity
H Vitamin D plays a major role in protection against inflammatory diseases by regulating the production of inflammatory cytokines, and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cells. Some Inflammatory diseases is atherosclerosis, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, chronic kidney disease, etc.
Cardiovascular Protection
Vitamin D helps regulate the system of blood pressure, the growth of vascular cells and fights inflammation. From research, vitamin D has been linked to heart health and the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
What is the difference between vitamin D3 and D2 and vitamin D?
Vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are the two main forms of vitamin D. Vitamin D2 is found in plants and yeast, while D3 comes from animal sources. Many supplements report vitamin D3 content. The daily dosage and maximum safe intake are the same whether it is vitamin D, D2 or D3. It is very important to pay attention to the content of supplements in vitamin D (or D3 or D2) as vitamin D if we exceed the safe limit (4000 IU units for adults) can cause very serious side effects
How much vitamin D do we need?
According to the American National Institutes of Health, adequate daily intake (AI) for vitamin D depends on age.
| Age | Vitamin D - Daily Intake (AI) |
|---|---|
| 0-12 months | 400 IU |
| 1-70 years | 600 IU |
| above 70 years | 800 IU |
The daily value (DV) for vitamin D for people over 7 is 800 IU.
The maximum allowable daily intake of Vitamin D for people over 9 years of age is 4000 IU .
Conversion of IU Units of vitamin D to Mcg
Online Vitamin D Calculator: conversion from IU units of vitamin D to micrograms (μg) of vitamin D
Sources of Vitamin D
There are very few foods that contain vitamin D, especially fatty fish and cod liver oil. Some butters, milks, vegan nut milks or breakfast cereals have added vitamin D. Mushrooms are interesting because when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, they produce vitamin D like humans. There are commercially available mushrooms that have been exposed to UV and have a high content of Vitamin D.
Animal Origin
Plant Origin
Animal Origin

1 tablespoon cod liver oil
1360 IU | 123 calories

Roasted trout 85 gr.
645 IU | 160 calories
1 egg
44 IU | 75 calories
Plant Origin

Mushrooms, exposed to UV light 100gr
944 IU | 22 calories

1 glass of almond milk, with the addition of vitamin D (250ml)
100-144 IU | 60 calories

1 glass of oat milk, with the addition of vitamin D (250 ml)
100-144 IU | 50 calories

1 tablespoon cod liver oil
1360 IU | 123 calories

Mushrooms, exposed to UV light 100gr
944 IU | 22 calories

Roasted trout 85 gr.
645 IU | 160 calories

1 glass of almond milk, with the addition of vitamin D (250ml)
100-144 IU | 60 calories
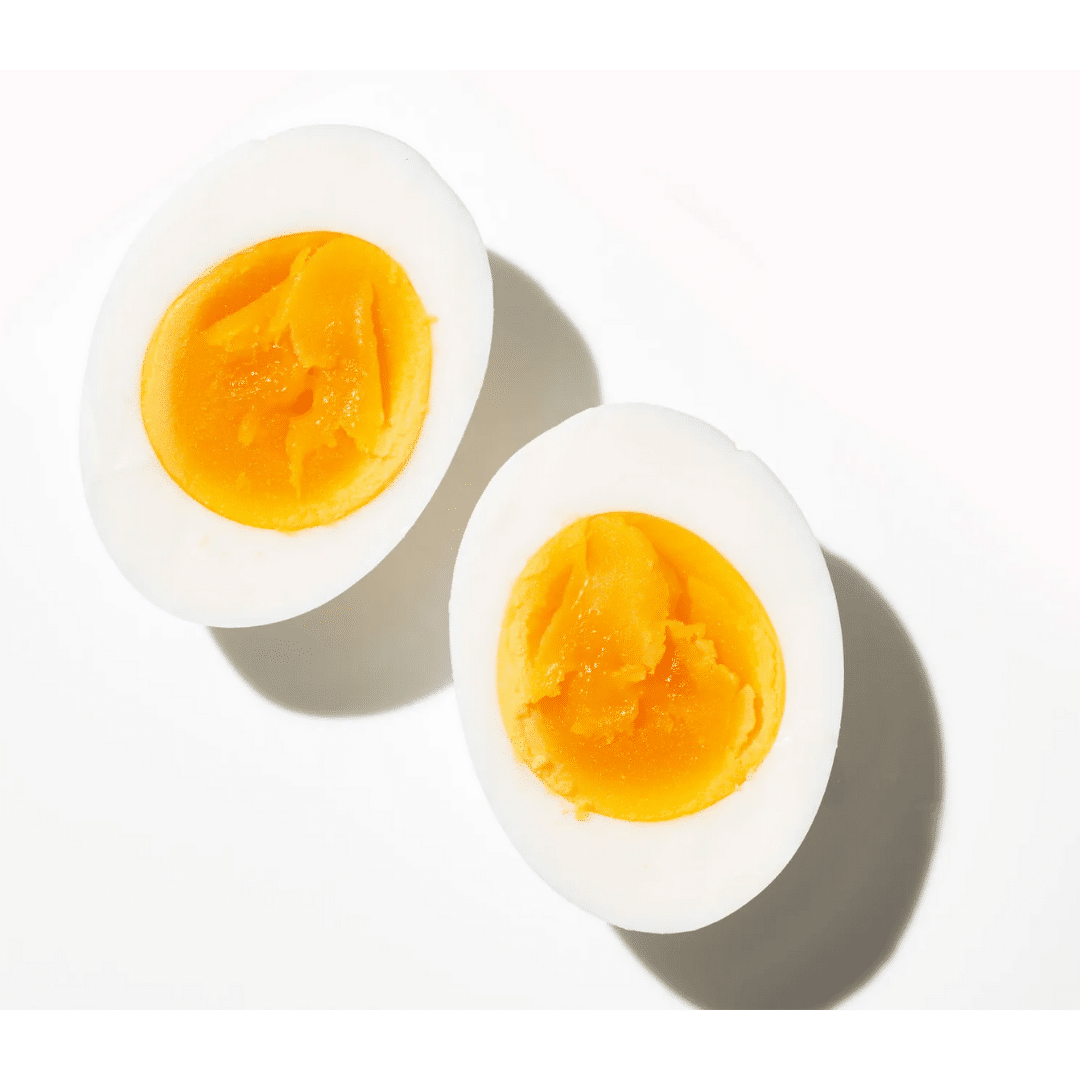

1 egg
44 IU | 75 calories

1 glass of oat milk, with the addition of vitamin D (250 ml) 100-144 IU | 50 calories
Vitamin D and the Sunlight

It takes just 10-15 minutes of sun exposure on the face and hands in Spring or Summer for our body to synthesize sufficient vitamin D.
The exposure should be in direct sunlight, without clouds, without glass interference and without the use of sunscreen.
The exposure time should not exceed 15 minutes due to the danger of long-term exposure to the sun.
The most often vitamin deficiency observed in the general population is the lack of vitamin D even in countries with high sunshine.
Who is most at risk for vitamin D deficiency?
- Breastfeeding babies
- Elderly
- People with dark skin
- Obese people
- People who have had gastric bypass surgery
- People with diseases that affect fat absorption
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D is probably the number 1 supplement you should consider taking if:
- you belong to a high risk group
- you do not consume cod liver oil or fatty fish daily
- you do not ensure adequate sun exposure (15 minutes with bare skin in direct sunlight, without sunscreen or glass interference) in Spring or Summer
- during the Autumn or Winter months
Vitamin D supplements are easily found in drops (usually tasteless) at a fair price, in any pharmacy ⚕ and the dose we will need to take daily (unless our doctor has recommended something else) is about 800 IU.
Overconsumption and Toxicity of Vitamin D
Symptoms of hypercalcaemia due to vitamin D toxicity
- Nausea, Vomiting
- Muscular weakness
- Neuropsychiatric disorders
- Pain
- Loss of appetite
- Excessive thirst
- Kidney stones
Extreme Symptoms of Vitamin D Toxicity
- Renal failure
- Soft tissue calcification
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Death
Vitamin D overconsumption can only occur by supplements as it is relatively impossible to consume such a large amount of fatty fish. Prolonged exposure to the sun also does not lead to overproduction of vitamin D because the thermal activation of provitamin D3 leads to the formation of other inactive forms, thus preventing high concentrations.
Excessive concentration of vitamin D leads to high absorption of calcium in the gastrointestinal tract, causing hypercalcemia in the body.
Hypercalcaemia, in turn, can lead to nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, neuropsychiatric disorders, pain, loss of appetite, dehydration, polyuria, excessive thirst and kidney stones.
In extreme cases, vitamin D toxicity causes kidney failure, calcification of soft tissues throughout the body (including coronary arteries and heart valves), heart arrhythmias and even death.
Serious cases of vitamin D toxicity have only been reported by:
- Consumption of dietary supplements containing excessive amounts of vitamin D due to manufacturing errors
- supplements taken in excessive amounts or incorrectly prescribed by doctors
Maximum Safe Limits of Vitamin D Intake
Most official health organizations around the world give a recommended daily intake of around 800 units for people over 7 years old. The upper limit for people over 9 years of age is 4000 units (IU) but it is best to stay at a recommended dose of less than 1000 IU unless your doctor tells you otherwise to avoid long-term effects of excessive calcium absorption.
| Age | Maximum Safe Intake of Vitamin D |
|---|---|
| 0-6 months | 1000 IU |
| 6-12 months | 1500 IU |
| 1-3 years | 2500 IU |
| 3-8 years | 3000 IU |
| above 9 years | 4000 IU |
Sources and Links
- Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals-U.S. Department of Health & Human Services- NIH (National Institute of Health)
- Vitamin D and inflammatory diseases- Kai Yin and Devendra K Agrawal -US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
- Vitamin D - School of Public Health -Harvard T.H. Tcan
- Vitamin D and Mushrooms -The Mushroom Council
